Why is Grain Stored in Silos: Understanding the Importance of Grain Storage

Grain storage plays a pivotal role in the agricultural sector, providing a means for farmers to safeguard their harvests. The question of why is grain stored in silos is multifaceted, delving into the advantages of using silos, the methods of grain storage, and its impact on the farming equipment landscape. In this article, we will embark on a comprehensive exploration of silos, their benefits, and their importance in modern agriculture.
The Definition of Silos in Agriculture
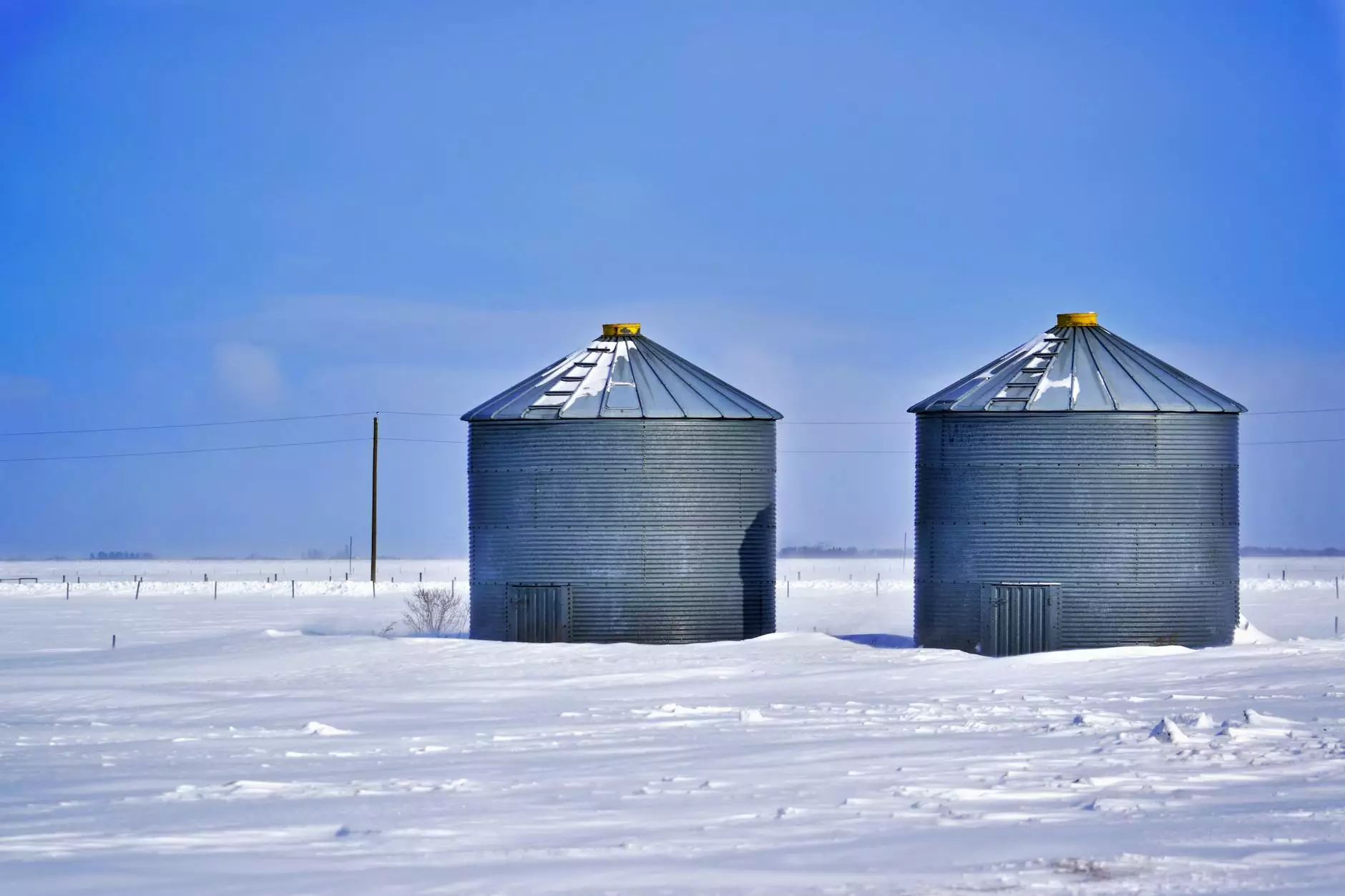
A silo is a towering structure designed for storing bulk materials, predominantly grain. Constructed from materials such as concrete, steel, or wood, silos are engineered to protect grains from environmental elements, pests, and spoilage. They come in various designs, including:
- Vertical Silos: These are cylindrical structures that stand tall and are the most common type found on farms.
- Horizontal Silos: Also known as bunkers, these are typically used for larger volumes of material.
- Bag Silos: Used for storage of smaller quantities, they consist of large plastic bags filled with grain.
Why is Grain Stored in Silos?
When examining why is grain stored in silos, we must consider the multiple benefits and reasons for adopting this storage method. Here are some key factors:
1. Protection from Environmental Factors
Grain is highly susceptible to moisture, heat, and fluctuations in temperature. A silo provides a controlled environment that:
- Prevents Moisture Ingress: Silos are designed to be airtight, which helps in minimizing moisture content.
- Regulates Temperature: The structure of a silo can help maintain a consistent temperature, preventing the grain from overheating.
2. Pest and Rodent Control
Insects and rodents can wreak havoc on stored grains. Silos provide a sealed environment that:
- Deters Pests: A well-sealed silo obstructs access to pests.
- Reduces Damage: By minimizing pest presence, silos protect grain integrity and quality.
3. Enhanced Storage Capacity
Silos are designed to store significant quantities of grain efficiently. The vertical design maximizes the area available for storage, enabling farmers to:
- Store More Grain: Vertical silos can hold large volumes on a smaller footprint.
- Utilize Space Efficiently: The compact design allows for significant storage without the need for expansive ground area.
4. Improved Grain Quality
Storing grain in silos contributes to maintaining its quality. The following factors enhance grain quality:
- Controlled Atmosphere: Silos can be equipped with ventilation systems that help maintain optimal conditions for stored grains.
- Reduced Spoilage: Properly sealed silos can reduce spoilage rates caused by aerobic bacteria.
Methods of Storing Grain in Silos
The methodology of grain storage in silos varies based on several factors such as the type of grain, the scale of operation, and technological advancements. Here’s an overview of the common methods:
1. Direct Filling
This method involves directly pouring freshly harvested grain into the silo without any drying or pre-treatment. It's often used for grains with adequate moisture content for storage.
2. Conditioning
Before storage, grains may undergo conditioning, which involves:
- Drying: Reducing moisture content to prevent spoilage.
- Cooling: Bringing grain temperature down to inhibit mold growth.
3. Aeration
Once grains are stored, aeration systems can be utilized to manage temperature and moisture levels actively. This helps maintain the right storage conditions throughout the storage period.
The Economic Impact of Grain Storage in Silos
Understanding why is grain stored in silos also includes recognizing its economic benefits. Here are key economic impacts:
1. Market Timing
Farmers can store grain until market conditions are favorable, allowing them to sell at optimal prices. This flexibility enhances profit margins significantly.
2. Better Inventory Management
With advanced storage options, farmers can maintain better inventory control, helping them to:- Reduce Waste: By managing quantities more effectively.- Plan for Demand: Aligning production and sale strategies based on market demand.
Safety Considerations in Grain Storage
While silos offer many advantages, safety must always be a primary concern. Grain handling and silo management pose risks such as:
- Engulfment Hazards: Workers can become trapped in grain if proper safety protocols are not implemented.
- Carbon Dioxide Exposure: The grain fermentation process generates carbon dioxide, which can be hazardous.
- Fire Risks: Dust accumulation within silos can create fire hazards.
Farmers and silo operators must educate workers about safety procedures, including:
- Conducting regular safety drills.
- Maintaining appropriate airflow within silos.
- Ensuring proper communication systems are in place.
Conclusion
In summary, silos serve as vital infrastructures in the agricultural landscape, safeguarding grains from environmental adversities and ensuring quality and stability in grain production and distribution. The exploration of why is grain stored in silos leads to a deeper understanding of the economic, safety, and quality aspects of grain storage. For businesses specializing in farming equipment and repair, like tsgcinc.com, understanding the significance of silos can enhance service offerings and cater to the evolving needs of modern agriculture. By investing in proper silo management and maintenance, farmers can ensure that their operations remain productive and sustainable.